Understanding Drainage Systems
Drainage systems are designed to remove excess water from surfaces, such as roofs, driveways, and landscapes, and direct it away from buildings and structures. These systems typically consist of a network of pipes, gutters, drains, and basins that collect and channel water to a safe discharge point, such as a storm drain or a retention pond.
Importance of Drainage Systems
Effective drainage systems are critical in protecting properties from water damage and flooding. Here are some key reasons why drainage systems are important:
Preventing Water Damage: Proper drainage prevents water from pooling around buildings and structures, reducing the risk of water infiltration and damage to foundations, walls, and basements.
Preventing Erosion: Drainage systems help prevent soil erosion by controlling the flow of water and preventing runoff from washing away topsoil and landscaping.
Protecting Landscapes: Proper drainage preserves the integrity of landscapes by preventing waterlogging and ensuring optimal growing conditions for plants and vegetation.
Preventing Flooding: Well-designed drainage systems help prevent localized flooding by efficiently managing surface water runoff during heavy rainstorms and snowmelt.
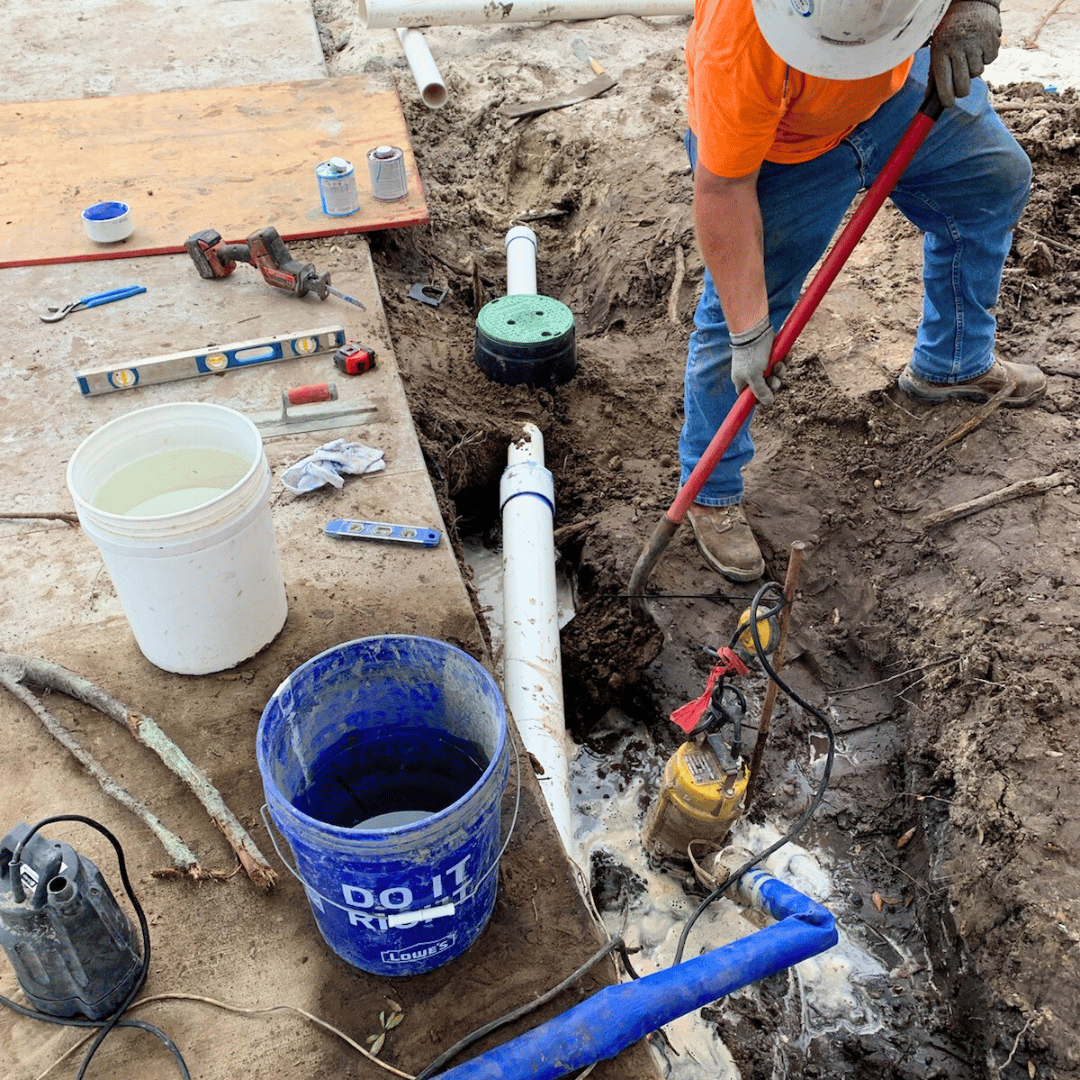
Installation of Drainage Systems
Proper installation is critical to the effectiveness of drainage systems. Here are the key steps involved in installing a drainage system:
● Site Assessment
Before installation, a thorough site assessment is conducted to identify areas prone to water accumulation and determine the best locations for drains, gutters, and downspouts.
● Design Planning
Based on the site assessment, a drainage plan is developed, outlining the layout of the drainage system, the types of components needed, and the flow paths for water discharge.
● Component Selection
The appropriate drainage components, such as pipes, catch basins, and grates, are selected based on factors such as soil type, water flow rate, and site conditions.
● Excavation and Installation
The installation process involves excavating trenches for pipes, installing drainage components, and backfilling with gravel or soil to provide stability and support.
● Testing and Inspection
Once installed, the drainage system is tested to ensure proper flow and functionality. Inspections are conducted to identify any defects or issues that need to be addressed.
Maintenance of Drainage Systems
Regular maintenance is essential to keep drainage systems functioning properly. Here are some maintenance tasks that should be performed regularly:
Clearing Debris
Remove leaves, twigs, and other debris from gutters, downspouts, and drains to prevent blockages and ensure proper water flow.
Inspecting for Damage
Regularly inspect drainage components for signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or corrosion, and repair or replace any damaged parts as needed.
Flushing Drainage Pipes
Periodically flush drainage pipes with water to remove sediment and debris buildup that can impede water flow.
Adjusting Slopes
Ensure that the slopes around buildings and structures are graded properly to direct water away from foundations and prevent water pooling.
Conclusion
Proper maintenance and installation of drainage systems are essential for efficient water management and the protection of properties from water damage and flooding. By understanding the importance of drainage systems and following best practices for installation and maintenance, property owners can ensure the long-term effectiveness and reliability of their drainage systems.