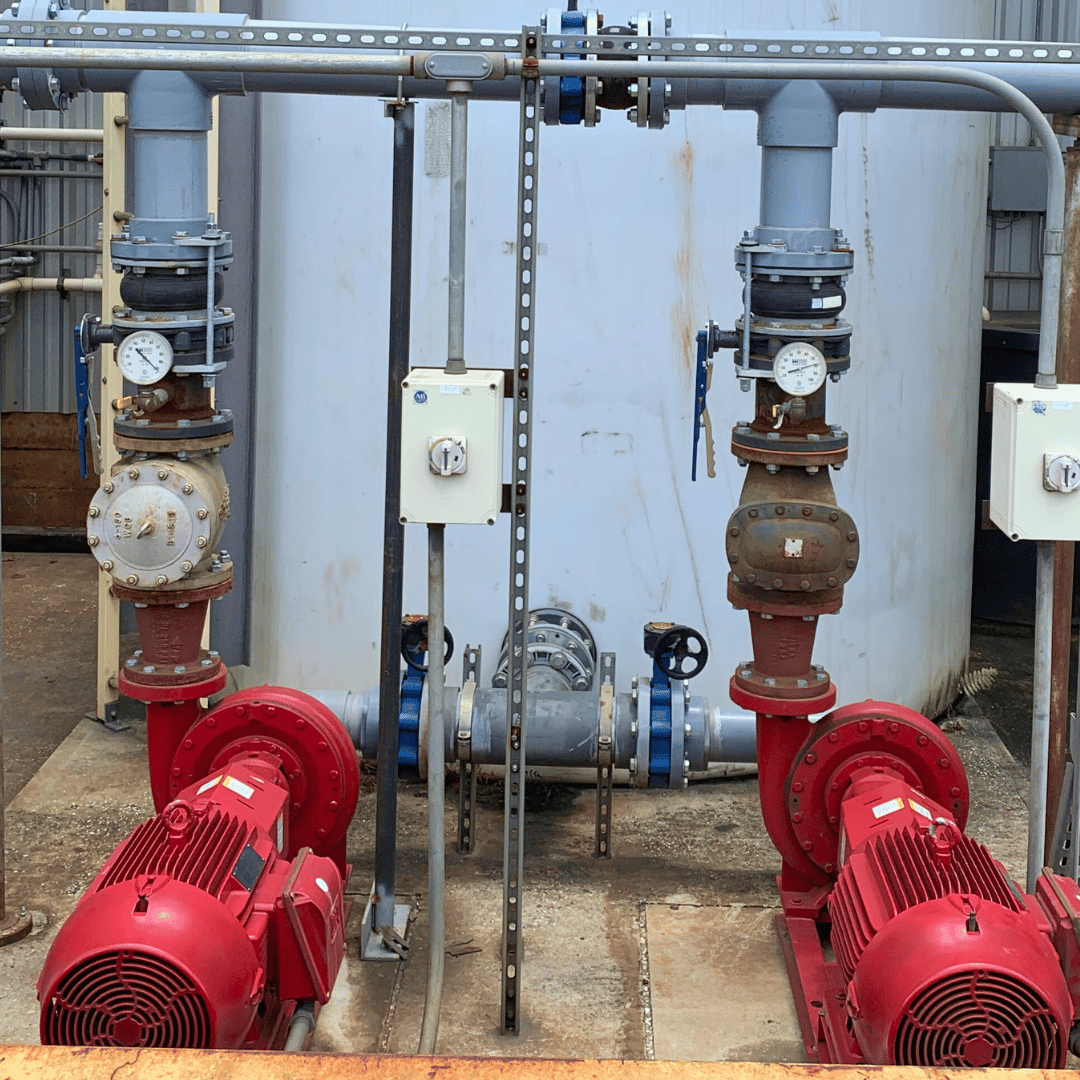
What is a Hydraulic Pump?
A hydraulic pump is a mechanical device designed to generate the flow or pressure of a hydraulic fluid within a hydraulic system. It serves as the heart of the hydraulic system, converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy to power cylinders, motors, and other hydraulic components. Hydraulic pumps are essential in applications where precise and powerful control of mechanical force is required, such as in construction equipment, manufacturing machinery, and automotive systems.
Types of Hydraulic Pumps:
Hydraulic pumps are classified into several types based on their operating principles, including:
- ● Gear Pumps: Gear pumps utilize the meshing of gears to generate flow. They are simple, compact, and cost-effective, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- ● Vane Pumps: Vane pumps employ sliding vanes to create flow. They offer smooth operation, low noise levels, and high efficiency, making them ideal for medium-pressure applications.
- ● Piston Pumps: Piston pumps use reciprocating pistons to generate flow. They offer high efficiency, precision control, and durability, making them suitable for high-pressure applications.
- ● Axial Piston Pumps: Axial piston pumps feature pistons arranged in a circular array around a central shaft. They offer excellent efficiency, high power density, and variable displacement capabilities, making them versatile for various applications.
Applications of Hydraulic Pumps:
Hydraulic pumps find extensive use across diverse industries and applications, including:
- ● Construction Machinery: Hydraulic pumps power excavators, bulldozers, loaders, and other heavy construction equipment, providing the force necessary for digging, lifting, and moving materials.
- ● Manufacturing Equipment: Hydraulic pumps drive presses, injection molding machines, metal forming equipment, and other manufacturing machinery, facilitating precise control and efficient operation.
- ● Aerospace Systems: Hydraulic pumps operate landing gear, flight control surfaces, and braking systems in aircraft, providing reliable and responsive hydraulic power for flight control and safety.
- ● Automotive Systems: Hydraulic pumps power steering systems, braking systems, and suspension systems in automobiles, enhancing vehicle maneuverability, safety, and comfort.
Maintenance and Optimization:
Proper maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and performance of hydraulic pumps. Key maintenance practices include:
- ● Regular Inspections: Scheduled inspections help identify wear, leaks, and other issues before they escalate into costly failures.
- ● Fluid Analysis: Regular fluid analysis monitors the condition of hydraulic fluid, identifying contaminants, degradation, and moisture levels that can affect pump performance.
- ● Seal and Gasket Checks: Inspecting seals and gaskets for wear and damage helps prevent fluid leaks and ensures proper pump operation.
- ● Temperature Monitoring: Monitoring pump temperatures helps detect overheating, which can indicate issues such as insufficient lubrication or excessive load.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, hydraulic pumps play a pivotal role in countless industrial and mechanical applications, providing the hydraulic power necessary for a wide range of tasks. Understanding the function, types, and maintenance requirements of hydraulic pumps is essential for optimizing performance, ensuring reliability, and minimizing downtime. By implementing proper maintenance practices and leveraging the appropriate type of hydraulic pump for each application, industries can maximize efficiency, productivity, and safety across various operations.